Table of Contents
What Is Voltage Stability/Voltage Stabilisation?
Voltage stability refers to the ability of an electrical system to supply a constant voltage, even if there are fluctuations or disturbances in the electricity grid caused by consumers, producers or, increasingly today, prosumers (‘prosumer’ = ‘producer’ + ‘consumer’). A stable voltage is crucial for the fault-free functioning of electrical consumers such as appliances in private households and machines in industrial plants. Voltage stabilisation is the process by which this voltage is continuously maintained at a stable level in order to minimise the effects of voltage fluctuations.
Official Definition
In the standard EN 50160 (“Voltage characteristics of electricity supplied by public distribution systems”), voltage stability is described as the ability of a system to keep voltage within a defined tolerance range, even during load fluctuations or external disturbances. These tolerances include ±10% of the nominal voltage.
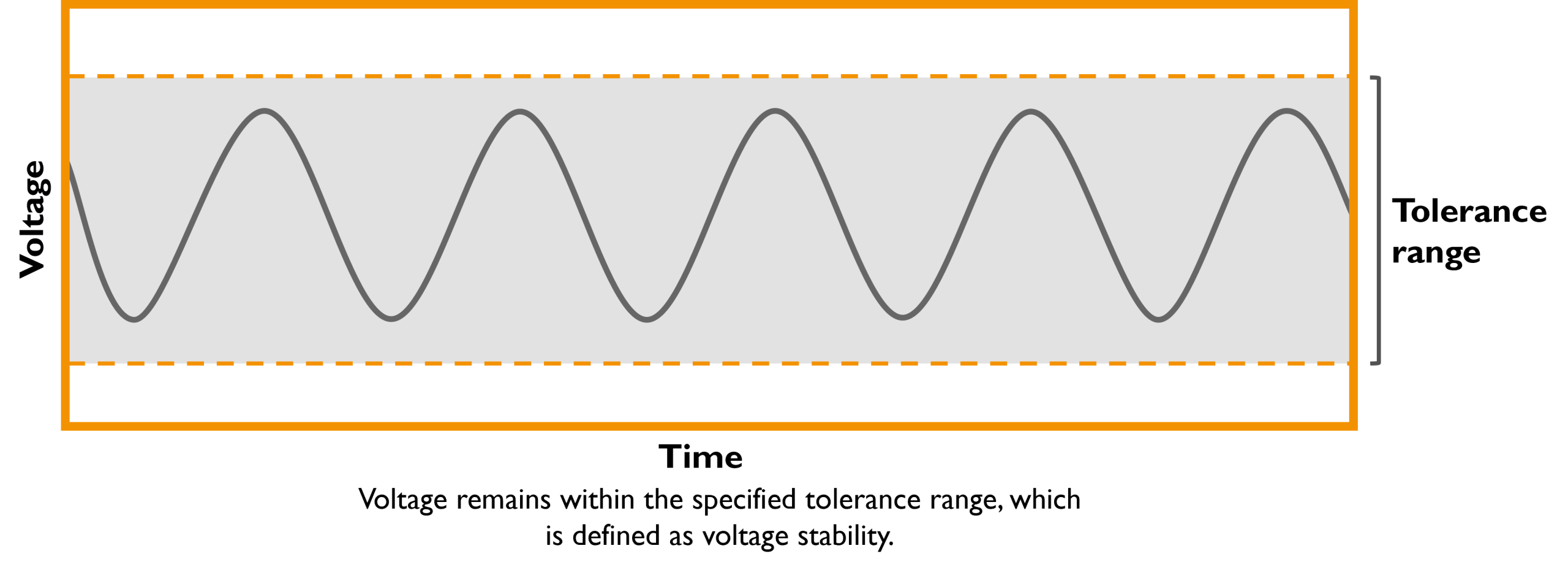
Why Is Voltage Stability Important?
Voltage stability is essential for efficient and safe power supply, especially in modern electricity systems, where a wide variety of devices and systems depend on constant voltage. Without a stable voltage, devices and machines cannot operate optimally, leading to energy losses, malfunctions, or even damage.
Why Is It Important?
- Avoiding damage to electrical devices: Unstable voltage can damage or even destroy sensitive devices such as computers, control systems, and industrial machines.
- Preventing failures in production facilities: Instability can lead to outages in production systems and massive economic losses (e.g. defective products).
- Optimizing energy efficiency: Voltage stabilisation balances fluctuations, leading to better energy utilization.
- Safety: Stable voltage ensures operational safety of the power grid and is particularly important for critical infrastructures like hospitals, data centres, or energy supply facilities.
- Legal obligations for energy providers: According to EN 50160, providers must supply electricity in a defined quality, especially in terms of voltage stability. If these are not met, customers can take legal action (e.g. claims for damages or contract enforcement), as poor voltage can lead to failures or damage.
What Can Disturb Voltage Stability?
Voltage stability can be disturbed by various factors, depending on how the grid is operated and what external influences affect the system.
Causes of Disturbances:
- Voltage fluctuations due to load changes
If the load in a grid changes rapidly (e.g. sudden rise or drop in consumption), the voltage cannot be adjusted immediately.
- Fluctuations in the power grid due to renewable generation technologies
Variable feed-in from renewables (wind, PV) can significantly affect voltage stability.
- Grid overload
Too many consumers at once can overload the grid and cause fluctuations – e.g. if many EV chargers are active in a neighbourhood simultaneously.
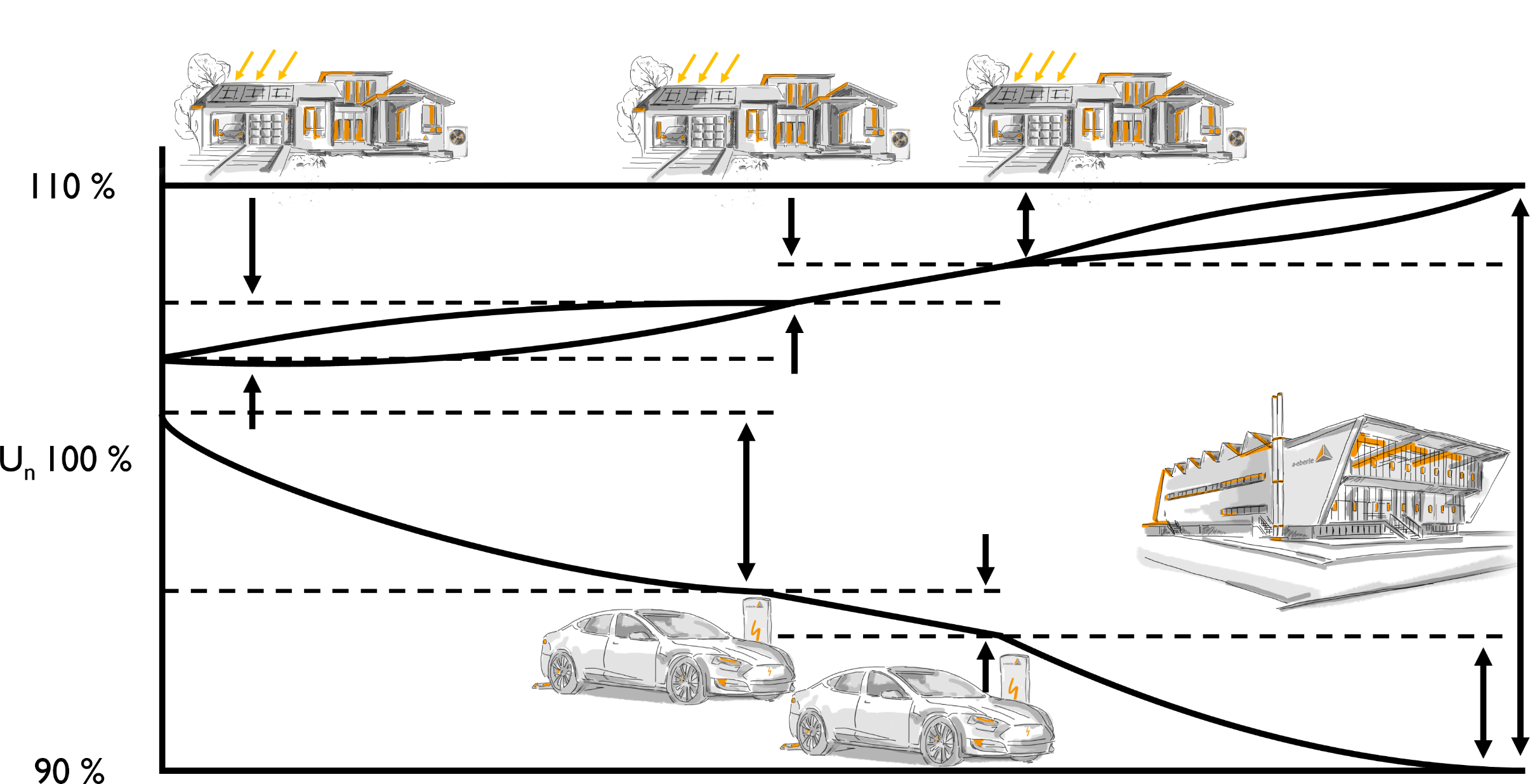
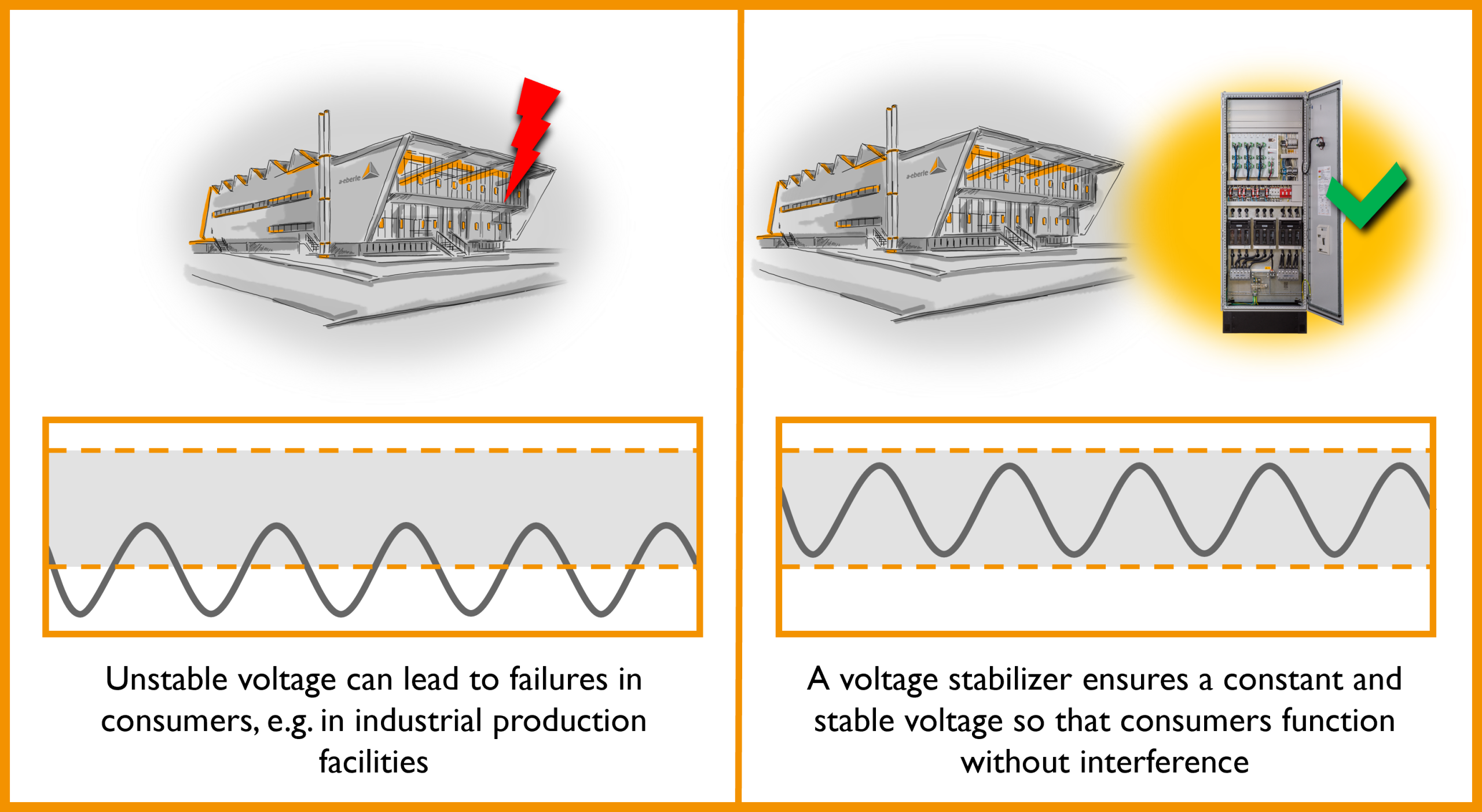
What Are the Negative Effects of Unstable Voltage?
Unstable voltage can cause serious issues for the power grid, for connected consumers, and for energy suppliers who are responsible for voltage stability.
Negative Consequences of Voltage Fluctuations:
- Damage to devices and machines: Over- or undervoltage can cause defects. Stabilised voltage is required in many modern devices; instability shortens their lifespan.
- Operational disruptions and failures: Especially in industry, stabilisation helps prevent downtime caused by irregular power.
- Higher maintenance and repair costs: Devices under unstable voltage need more maintenance and repairs.
- Increased efficiency: Devices work most efficiently at rated voltage (e.g. 400 V L-L or 230 V L-N), which is only possible with stable voltage.
How Can Voltage Be Stabilised?
Voltage stabilisation is a key aspect of energy supply, especially in complex electrical networks where voltage fluctuations can disrupt the operation of sensitive devices and systems. Voltage stability can be achieved with the appropriate control technology, which is specially adapted to the different voltage levels in the energy supply network: high, medium and low voltage. For example, A. Eberle offers the LVRSys® low-voltage control system for effective voltage stabilisation in the low-voltage range, while the REGSys® voltage control system is used in the high- and medium-voltage range.
High and Medium Voltage: REGSys®
In medium voltage (1 kV – 36 kV) and high voltage (above 36 kV), stabilisation is crucial for utilities, as large energy flows interact with many consumers and producers. Stabilisation is often done using voltage regulators like REGSys®, which quickly adjust voltage when it is too high or too low.

Our REGSys® voltage regulation system is used to ensure voltage stability on transformers and in electricity networks with variable loads. This helps to keep the voltage at a constant level and thus guarantee voltage stability, especially when the load changes.

REGSys®
Our »REGSys® voltage regulation system« is specially designed to compensate for voltage fluctuations and voltage drops in high and medium-voltage grids. In addition to the automatic regulation, monitoring and supervision of transformers with on-load tap-changers, REGSys® can be supplemented with additional functions such as current influence (e.g. compensation of line impedances) or parallel operation, depending on the individual application.
Low Voltage: LVRSys®

In low voltage (400 V L-L or 230 V L-N), Stabilisation is crucial for household and industrial consumers. LVRSys® is specially designed for this and provides an effective solution to keep voltage within the standard-compliant range.
By using LVRSys®, stability can be ensured and the risk of damage due to unstable voltage minimised – especially in networks with frequent fluctuations caused by peak loads, PV systems, EV charging, or heat pumps.
Developed to address voltage problems in low-voltage grids due to electromobility, photovoltaics, heat pumps, or long cable runs. It’s a cost-effective and flexible alternative to expensive and time-consuming grid expansion. Easily integrable and maintenance-free.
The use of LVRSys® ensures voltage stability in the low-voltage range and minimises the risk of damage caused by unstable voltages. This system is particularly useful in networks where voltage fluctuations occur frequently, for example due to peak loads or irregular load distribution caused by photovoltaic systems, charging stations/wall boxes or heat pumps.

LVRSys®
The »LVRSys® low-voltage control system« was specially developed to solve voltage stability problems in the low-voltage grid due to the integration of electromobility, photovoltaics and heat pumps or long transmission lines. It is an economical and flexible alternative to costly and time-consuming line extensions. The system is tried and tested, easy to integrate into the grid and maintenance-free.
Differentiation: LVRSys® vs. Other Common Voltage Stabilisation Methods
Some commonly used voltage stabilisation systems – such as those based on conventional compensation or regulation methods – are primarily suitable for local applications near industrial facilities or transformer stations. These systems stabilise voltage at the feed-in point, but their effect is limited to the immediate area and their integration into existing power distribution networks is often restricted.
LVRSys® takes a different approach:
The system is installed along the low-voltage line, for example at the end of the line or at points where voltage drops actually occur. This allows for area-wide, decentralised voltage regulation and makes it ideal for stabilising grids with PV systems, heat pumps or EV charging infrastructure.
Voltage stabilizers
Voltage stabilizers detect fluctuations and correct them immediately to ensure constant voltage. They continuously monitor and adjust to ideal values, making them useful for small grids or specific industrial applications.
However, they reach their limits in large or complex grids, like those in public power systems. Their limited scalability and slower response to voltage dips make them unsuitable in many cases. They also lack the flexibility to handle dynamic load changes and often can’t integrate with modern grid management systems.
Advantages of LVRSys® for Voltage Stabilisation
- Acts deep in the LV-grid where voltage becomes unstable – not just at the substation transformer
- Ideal for distribution networks with decentralised generation and high dynamics
- Easy grid integration without reconstruction – maintenance-free, efficient, scalable
Do You Have Any Questions About Our Voltage Stabilisation Solutions?
We Offer Solutions for All Voltage Levels.
Contact Us Now




